What are the 6 Rs of migration
What are the 6 Rs of migration: Strategies for Successful Cloud Migration
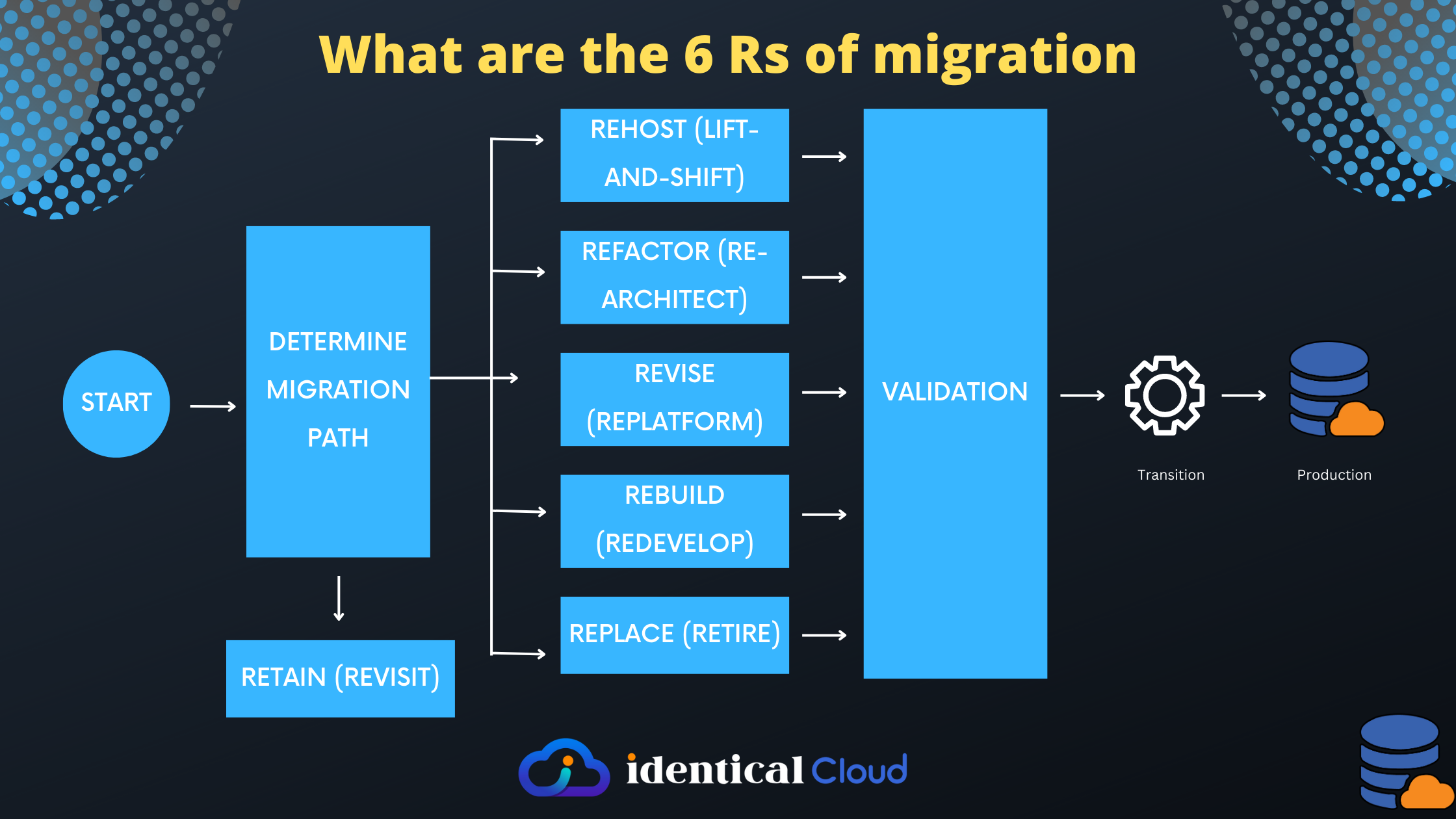
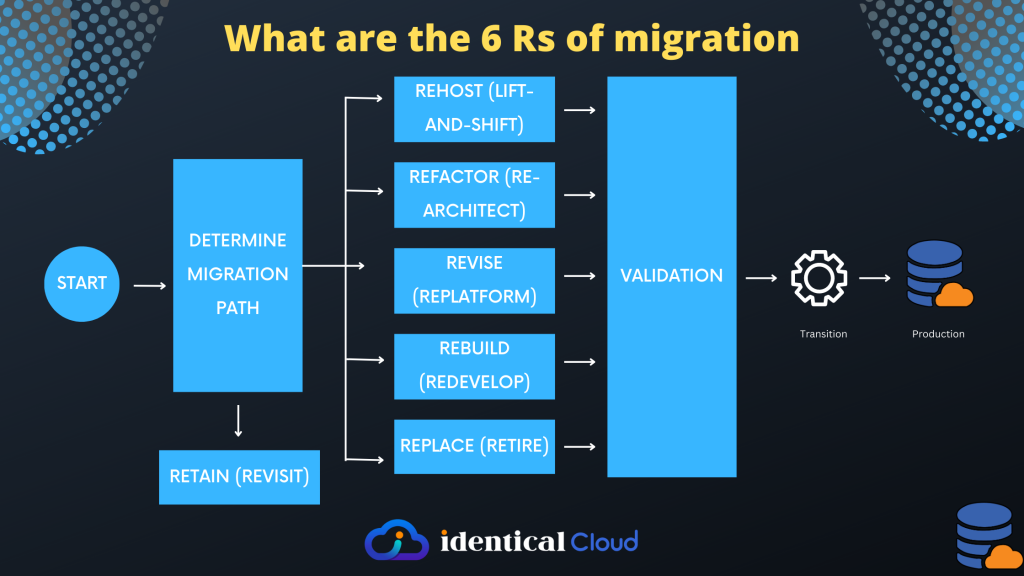
Cloud migration is a crucial step for organizations looking to leverage the benefits of cloud computing. It involves moving applications, data, and infrastructure from on-premises or legacy systems to the cloud. To ensure a smooth and successful migration, organizations often adopt one of the 6 Rs of migration: Rehost, Refactor, Revise, Rebuild, Replace, or Retain.
In this blog post, we will explore each migration strategy in detail, along with its advantages and considerations.
Rehost (lift-and-shift):
Rehosting, also known as lift-and-shift, involves migrating applications to the cloud without making significant changes to the underlying architecture. The application is moved as is, typically running on virtual machines in the cloud environment. Advantages of rehosting include faster migration with minimal disruption, cost savings, and maintaining application compatibility. However, it may not fully leverage the benefits of cloud-native services and optimizations.
Refactor (re-architect):
Refactoring, also referred to as re-architecting, involves making significant changes to the application architecture to align it with cloud-native principles and services. It may involve redesigning and rewriting parts of the application to take advantage of scalable and resilient cloud services. The benefits of refactoring include improved performance, scalability, and cost optimization. However, it requires more effort, time, and expertise compared to rehosting.
Revise (replatform):
Revising, or replatforming, involves migrating applications with minor modifications to utilize cloud-specific features and services. It may involve updating the underlying infrastructure or modifying the application to optimize performance and take advantage of cloud capabilities. This approach offers a balance between effort and benefits, allowing organizations to leverage some cloud advantages while minimizing the level of effort required for migration.
Rebuild (redevelop):
Rebuilding, or redeveloping, involves completely rewriting the application using cloud-native technologies and services. This approach allows organizations to fully utilize the scalability, agility, and flexibility of the cloud. It offers the highest level of optimization and enables the adoption of modern development practices. However, it requires significant development effort and may involve longer migration timelines.
Replace (retire):
Replacing involves migrating applications by replacing them with commercially available software-as-a-service (SaaS) or cloud-native solutions. Instead of migrating the existing application, organizations opt for a different software solution that meets their requirements. This strategy can be beneficial when there are suitable SaaS options available that offer better functionality and cost-effectiveness. However, it may require changes in business processes and user training.
Retain (revisit):
Retaining involves keeping certain applications on-premises or in the existing infrastructure and not migrating them to the cloud. This approach is chosen when applications are not suitable for the cloud due to compliance, security, or cost considerations. Retaining allows organizations to focus on other migration strategies for suitable applications while maintaining critical systems in their current environment.
Considerations for Migration:
- Cost: Assess the cost implications of each migration strategy, including upfront expenses, ongoing operational costs, and potential savings in the long run.
- Complexity: Evaluate the complexity and level of effort required for each migration strategy based on application dependencies, data transfer, and required modifications.
- Performance: Consider the performance implications of each strategy, such as scalability, availability, and response times, to ensure optimal application performance in the cloud environment.
- Timeframe: Assess the migration timeline and prioritize applications based on business needs, dependencies, and criticality.
- Skillset: Evaluate the required skills and expertise for each migration strategy to ensure the availability of the necessary resources for a successful migration.
The 6 Rs of migration provide a framework for organizations to choose the most appropriate strategy for their cloud migration journey. Whether it’s rehosting for a quick and cost-effective migration or rebuilding for maximum cloud-native optimization, each strategy has its advantages and considerations. Organizations should carefully evaluate their applications, business requirements, and available resources to determine the best approach and ensure a successful transition to the cloud.
